The seamless movement of goods and services from point A to point B is a cornerstone for success. Logistics management is at the heart of this intricate operation, the unsung hero orchestrating the flow of resources across various channels to ensure optimal efficiency.
But what is logistics management, and why does it serve as the backbone of business efficiency? Keep on reading to find out!
Optimize Your Deliveries Before They Fall Through the Cracks
Get real-time updates, optimize routes, and improve operational efficiency with Detrack

What is Logistics Management?
Logistics management refers to planning, coordinating, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
It integrates various activities such as procurement, transportation, inventory management, warehousing, material handling, packaging, and security.
The primary goal of logistics management is to ensure that the right product is delivered to the right place, at the right time, in the right condition, and at the right cost, optimizing the supply chain and effectively meeting customer demands.
Efficient logistics management often reduces costs, improves customer satisfaction, and enhances overall business performance.
Types of Logistics Management
Inbound Logistics
This facet of logistics management involves overseeing and managing all activities associated with sourcing, acquiring, transporting, and storing raw materials, components, or goods that come into an organization.
It includes supplier relationship management, inventory control, transportation scheduling, and warehouse management. Inbound logistics aims to ensure a smooth and efficient flow of materials to support production or further processing within the organization.
Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics revolves around the efficient and effective movement of finished products or services from production to the end consumer or distribution centers. This aspect encompasses order fulfillment, transportation planning, warehousing, and customer delivery.
The goal is to meet customer demands promptly, accurately, and at the lowest possible cost. Outbound logistics often involves optimizing distribution networks, selecting appropriate transportation modes, order processing, and managing relationships with carriers and distributors to ensure timely and accurate deliveries while minimizing transportation costs.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics deals with the processes involved in managing returned products, recycling materials, or appropriately disposing of goods. It encompasses product returns, refurbishment, recycling, remanufacturing, or responsible disposal of items.
This aspect of logistics management is critical for managing product recalls, addressing product defects, managing surplus inventory, and implementing sustainable practices.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics involves outsourcing certain logistics and supply chain management aspects to external service providers. Companies engage with 3PL providers for various services such as transportation, warehousing, distribution, freight forwarding, and inventory management.
Outsourcing logistics functions to specialized providers can offer cost efficiencies, expertise, and flexibility, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies. 3PL providers leverage their expertise, technology, and networks to optimize supply chain operations, improve service levels, and enhance overall logistics performance for their clients.
Distribution Logistics
Distribution logistics focuses on the efficient and effective management of storage facilities, inventory control, and the movement of goods within distribution centers or warehouses. It involves inventory tracking, order picking, packing, and shipping products to fulfill customer orders.
Distribution logistics aims to streamline operations within distribution centers to optimize space utilization, minimize handling costs, reduce order processing times, and ensure accurate and timely deliveries.
Green Logistics
Green logistics, also known as sustainable logistics, emphasizes environmentally friendly practices within logistics and supply chain operations. These include reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste generation, utilizing eco-friendly transportation modes, optimizing packaging materials for recyclability, and adopting renewable energy sources.
Green logistics aims to reduce the environmental impact of logistics activities while striving for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It involves implementing strategies like route optimization, using alternative fuels or energy-efficient vehicles, promoting recycling and waste reduction, and complying with environmental regulations to create a more sustainable supply chain ecosystem.

What Does the Logistics Management Process Involve?
Facility Safety and Efficiency Inspection
Logistics facilities require regular safety and efficiency inspections, including warehouses, distribution centers, and transportation hubs. These assessments involve thorough checks for compliance with safety regulations, identifying potential hazards, ensuring proper equipment storage, and optimizing the layout for streamlined operations.
Equipment Inspection
Logistics heavily relies on various types of equipment and machinery for tasks such as handling, packaging, and transporting goods. Regular inspections of this equipment are vital to identify wear and tear, potential breakdowns, or malfunctions that might disrupt operations.
Inventory Control to Balance Stock and Demand
Effective inventory management is critical in logistics. It involves sophisticated strategies to forecast demand, optimize stock levels, and prevent overstocking or stockouts. Balancing stock and demand requires the implementation of inventory control methods, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems, ABC analysis, and employing inventory management software to track stock levels in real time.
ISO Container Inspections
In international logistics, particularly shipping, adhering to ISO container standards is imperative. Inspections ensure that shipping containers comply with specific dimensions, structural integrity, and safety standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Order Fulfillment Process
Managing the order fulfillment process involves orchestrating various stages, from order placement to delivery. This encompasses order processing, picking items from inventory, packing, labeling, and arranging shipping. To optimize this process, businesses employ technologies like warehouse management systems (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software for efficient order tracking, inventory visibility, and ensuring accurate and timely customer deliveries.
Managing Transactions and Feedback
Logistics management also involves overseeing financial transactions related to the movement of goods, including invoicing, billing, payments, and maintaining records. Feedback from customers, suppliers, and stakeholders is essential for continuous improvement. Analyzing feedback allows for process adjustments, addressing issues promptly, and enhancing overall service quality and customer satisfaction.
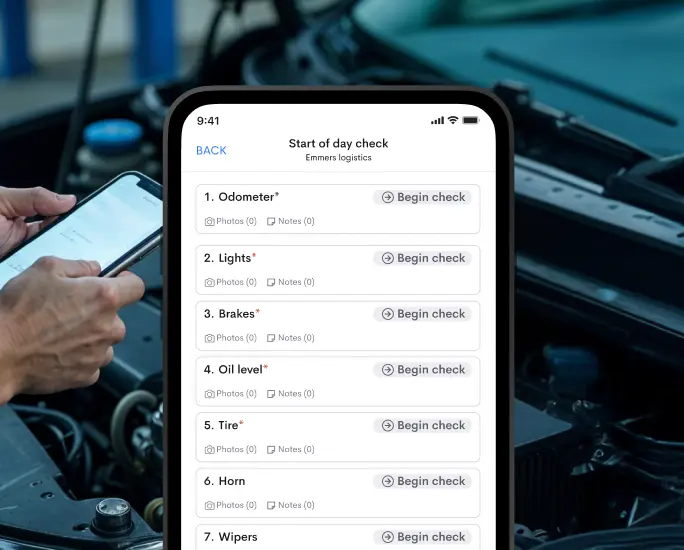
Vehicle Maintenance Checks
Vehicles play a pivotal role in logistics and transportation. Regular maintenance checks, including inspections, servicing, and repairs, ensure the fleet’s optimal performance and safety. Properly maintained vehicles reduce the risk of breakdowns, enhance fuel efficiency, and contribute to on-time deliveries, ultimately positively impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Regular Safety Compliance Checks
Adherence to safety regulations and industry standards is non-negotiable in logistics. Regular safety compliance checks involve assessing and ensuring that operations, facilities, equipment, and processes meet regulatory requirements. This includes employee safety training, proper handling of hazardous materials, maintaining workplace hygiene, and implementing safety protocols to mitigate risks and maintain a safe working environment.

Challenges in Logistics Management
- Ensuring Top-Notch Customer Service: Meeting customer expectations for timely deliveries, order accuracy, and overall satisfaction poses a significant challenge. Customers expect faster delivery times and real-time tracking, which requires a robust logistics infrastructure and efficient processes. Balancing speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness while maintaining service excellence is an ongoing challenge in logistics.
- Controlling Transportation Costs: Transportation expenses, including fuel costs, carrier rates, infrastructure charges, and fluctuating market conditions, significantly impact logistics costs. Optimizing transportation routes, mode selection (air, sea, road, or rail), and negotiating favorable contracts with carriers or 3PL providers is crucial. Rising fuel prices, unexpected surcharges, and capacity constraints also contribute to the challenge of managing transportation costs effectively.
- Effective Planning and Risk Management: Logistics operations involve numerous variables, including demand fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, natural disasters, geopolitical events, and unforeseen disruptions. Balancing supply and demand, developing contingency plans, implementing robust risk management strategies, and building resilience in the supply chain are essential to mitigate potential disruptions and maintain continuity.
- Maintaining Supplier/Partner Relationships: Collaboration with suppliers, vendors, and partners is integral to logistics management. Challenges arise in managing these relationships effectively, ensuring timely and quality supplies, managing lead times, and aligning goals and processes among different stakeholders in the supply chain. Communication, reliability, and mutual trust are critical to sustaining strong partnerships.
- Government and Environmental Regulations: Compliance with ever-changing government regulations, customs requirements, trade restrictions, and environmental standards adds complexity to logistics operations. Adapting to new regulations, navigating trade barriers, ensuring proper documentation, and incorporating eco-friendly practices to comply with environmental regulations pose challenges. Striking a balance between meeting compliance obligations and operational efficiency is a continuous challenge in logistics management.
8 Tips and Best Practices for Effective Logistics Management
1. Make a Solid Plan
A comprehensive logistics plan forms the foundation of efficient operations. This involves mapping the entire logistics process, including procurement, storage, transportation, and delivery. Incorporate demand forecasting to anticipate customer needs and establish inventory levels accordingly.
Consider factors like lead times, supplier capabilities, seasonal fluctuations, and market trends while planning. Moreover, it ensures clear communication and alignment of objectives among different departments involved in the logistics process.
2. Have a Contingency Plan
While a solid plan is essential, contingency is equally crucial. Unexpected disruptions such as natural disasters, supplier issues, or transportation delays can impact logistics operations.
Develop backup strategies, alternative suppliers, redundant transportation routes, and emergency response protocols to mitigate risks and ensure continuity of operations during unforeseen events.
3. Hire a Logistics Manager with Strong Interpersonal Skills
A proficient logistics manager should possess technical expertise and strong interpersonal and leadership skills. They must effectively communicate with various stakeholders, negotiate with suppliers, manage a diverse team, and troubleshoot problems efficiently.
Their ability to build and maintain relationships with partners, clients, and internal teams greatly influences the success of logistics operations.
4. Automate Your Systems
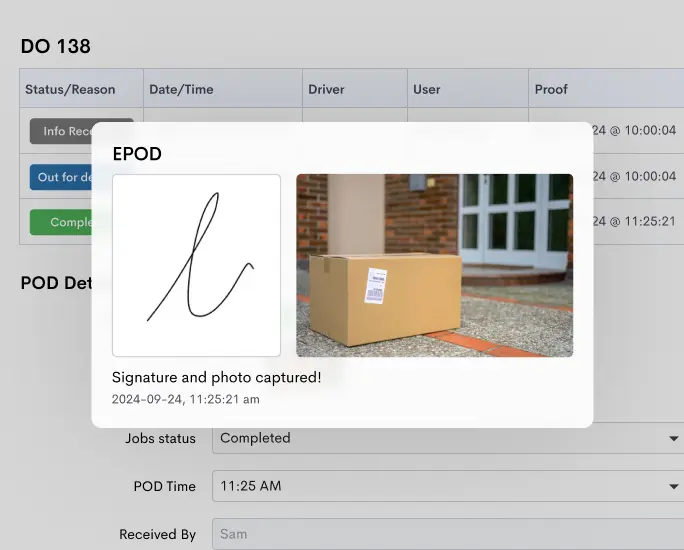
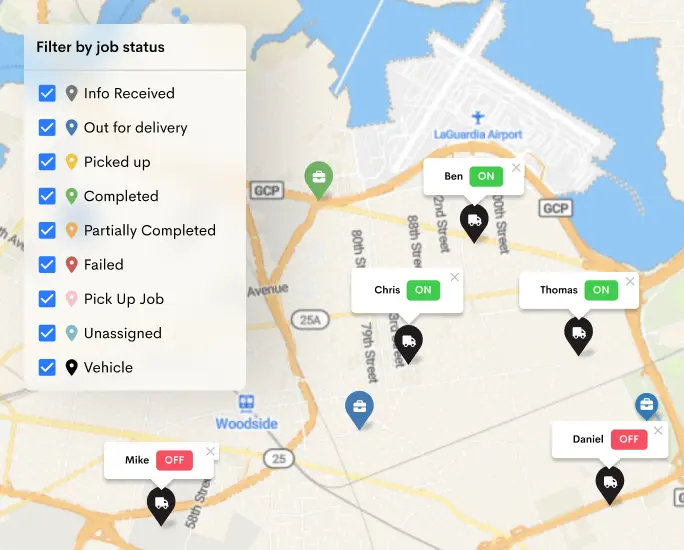
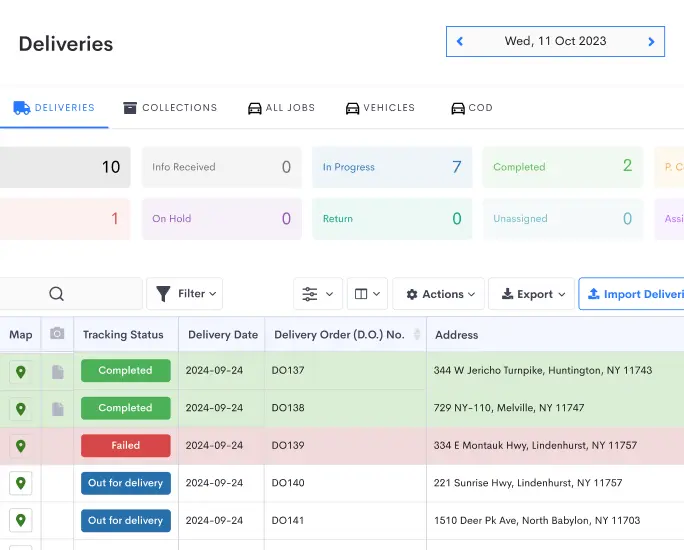
Automation streamlines logistics processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Utilize technology-driven solutions like Detrack, a platform for tracking deliveries and managing fleets. This platform provides real-time visibility, route optimization, and proof of delivery.
Integrating such systems into logistics operations helps automate tasks, improves accuracy, and enhances overall performance. Detrack’s capability to track and monitor deliveries, integrate with various systems, and streamline last-mile delivery contributes significantly to logistics efficiency.
5. Learn from Mistakes
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by analyzing past mistakes or inefficiencies. Conduct thorough post-mortems of logistics-related issues, gather stakeholder feedback, and use data analytics to identify patterns and root causes.
Implement corrective actions to prevent similar issues in the future and encourage a proactive approach to solving problems.
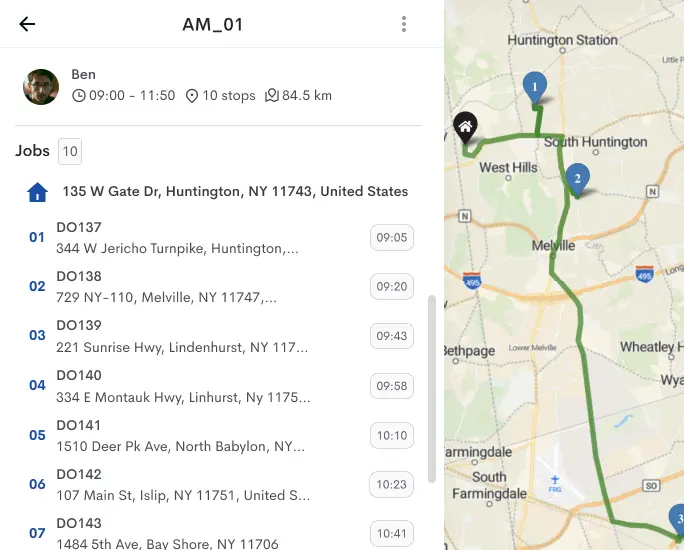
6. Effective Transportation Management
Efficient transportation management is pivotal in logistics. Optimize transportation by employing cost-effective packaging, selecting the most efficient delivery routes, and leveraging technology for route optimization.
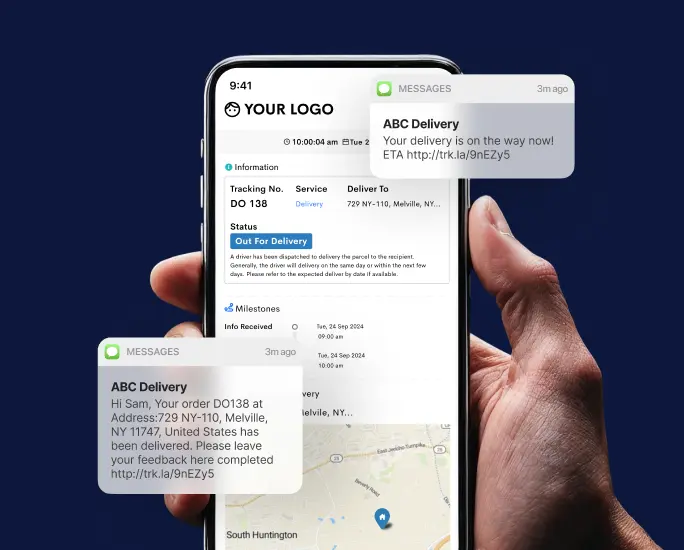
Solutions like Detrack can enhance last-mile delivery, minimize delays, and improve customer satisfaction by providing real-time updates and proof of delivery.
7. Warehouse and Inventory Management
Utilize advanced systems like Detrack, which integrates seamlessly with various systems (ERP, CRM, e-commerce platforms) for efficient warehouse and inventory management. This integration ensures smooth data flow, accurate inventory tracking, and streamlined order fulfillment.
Additionally, it leverages technologies for warehouse optimization, such as RFID systems or automated inventory control, to improve accuracy and speed in handling goods.
8. Measure and Continuously Improve
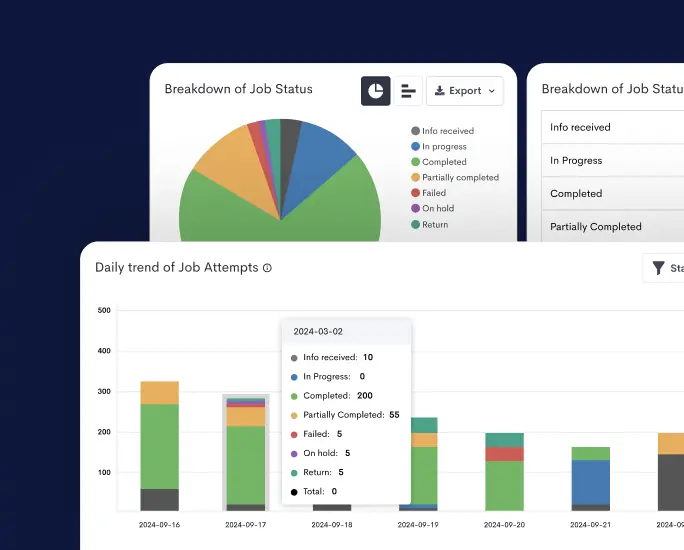
Utilize the reporting and analytics features of solutions like Detrack to monitor KPIs, track delivery performance, and identify areas for enhancement.
Detrack’s dashboard and reporting tools offer insights into delivery statuses, performance metrics, and customer feedback, allowing for data-driven decision-making. Review metrics regularly, analyze trends, and adapt strategies to continuously improve logistics operations.
Improve Logistics Management for Higher Customer Experience and Operational Efficiency
Improving logistics management is crucial for achieving higher levels of customer experience and operational efficiency. Businesses can significantly enhance their logistics operations by leveraging advanced tools and strategies like Detrack.
Detrack, as mentioned earlier, plays a pivotal role in optimizing logistics processes. Its capabilities in tracking and monitoring deliveries, managing fleets, streamlining last-mile delivery, and providing real-time updates contribute directly to improved customer experiences.
The platform’s integration with various systems ensures seamless data flow, enhancing operational efficiency and warehouse and inventory management accuracy.
Moreover, its reporting and analytics features enable businesses to make data-driven decisions, identify bottlenecks, and continuously improve logistics operations for better efficiency and service quality.
Optimize Your Deliveries Before They Fall Through the Cracks
Get real-time updates, optimize routes, and improve operational efficiency with Detrack