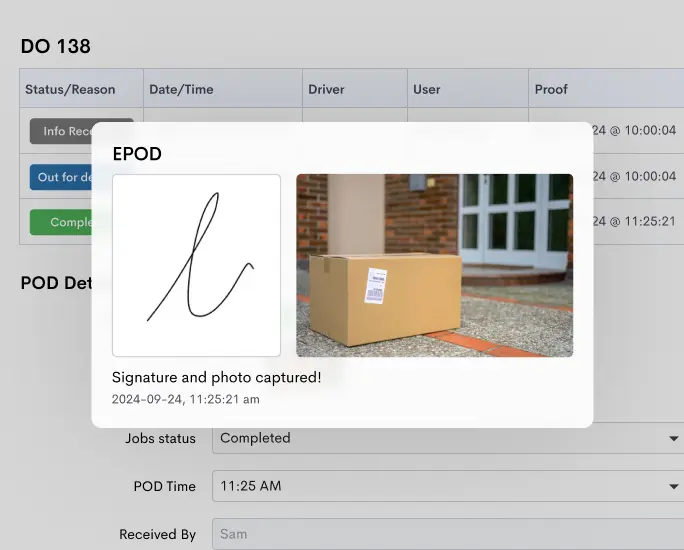
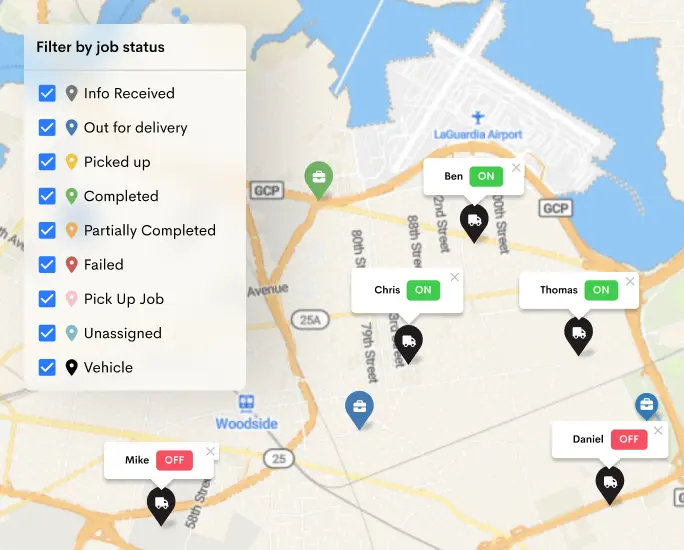
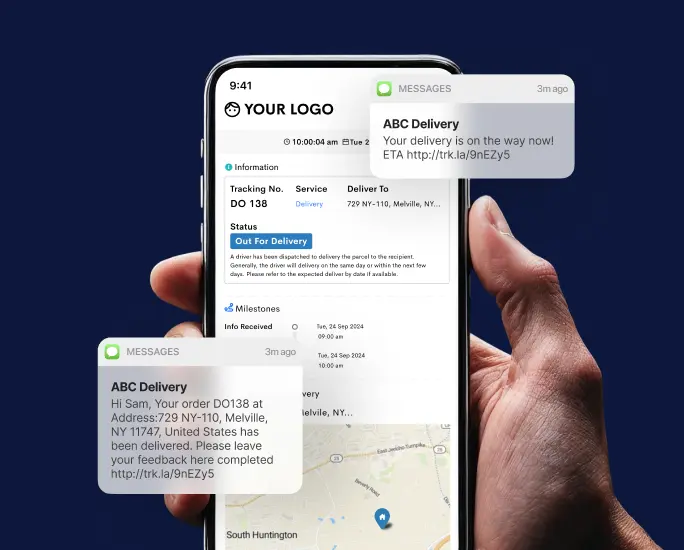
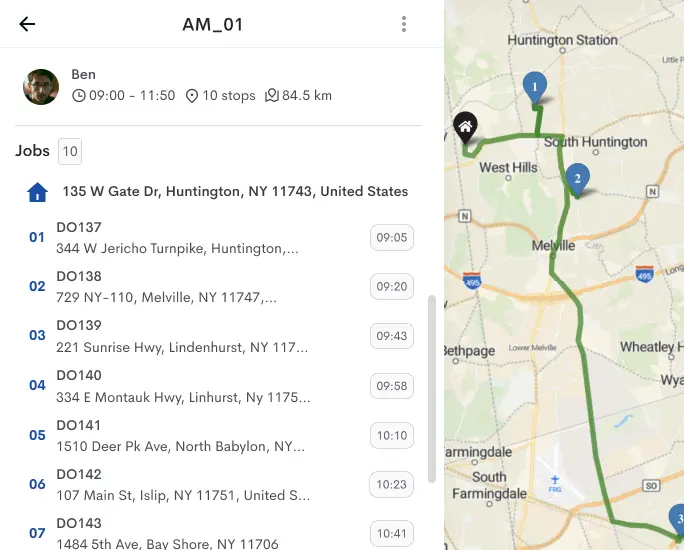
Cold chain logistics management plays a vital role in preserving the quality, efficacy, and safety of temperature-sensitive goods like perishable foods, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines.
Maintaining the optimal temperature throughout the supply chain is crucial from farm to fork and manufacturing plants to hospitals.
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of cold chain logistics and the key elements that ensure the freshness and integrity of these valuable products.
Join us as we delve into the challenges faced by logistics professionals and the innovative solutions and emerging technologies driving efficiency in this complex and important field.
What is Cold Chain Logistics?
Cold chain logistics refers to the specialized management of temperature-sensitive goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring they maintain their required temperature conditions to preserve their quality, efficacy, and safety.
It encompasses transporting, storing, and handling perishable and temperature-sensitive products, such as food items, pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and biotechnological products.
Cold chain logistics involves a series of controlled temperature environments, refrigeration equipment, monitoring systems, and protocols to maintain the desired temperature range from the point of origin to the final destination.
The goal is to prevent any temperature excursions that could compromise the integrity and effectiveness of the goods, ultimately ensuring that they reach consumers or end-users in optimal condition.
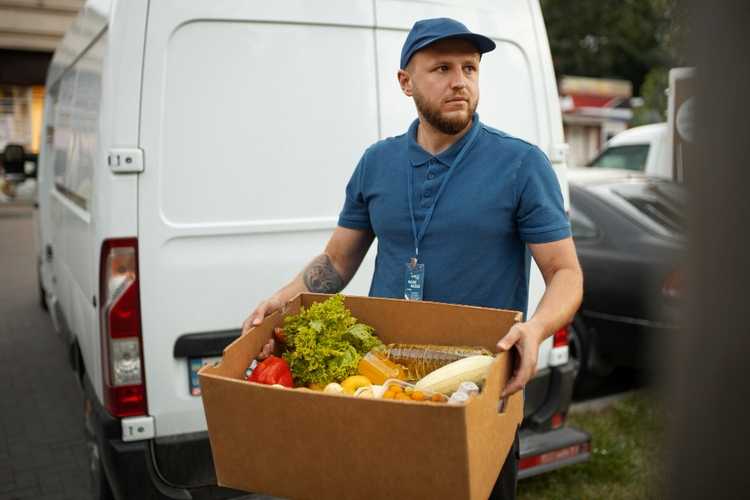

Key components of cold chain logistics
Temperature monitoring and control
Maintaining the desired temperature range is essential to prevent any temperature excursions that could compromise the quality and effectiveness of temperature-sensitive products.
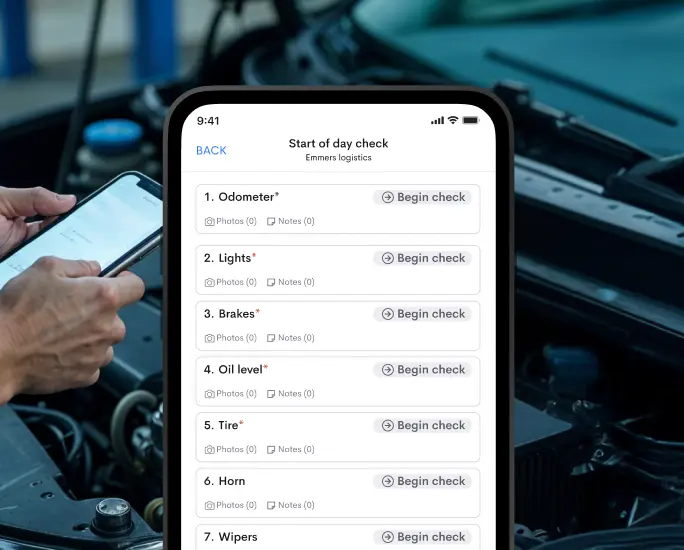
Temperature monitoring devices, such as data loggers or real-time sensors, are strategically placed along the supply chain to monitor and record temperature data continuously. This data helps identify deviations and allows timely interventions to rectify issues.
Advanced monitoring systems may even provide real-time alerts and notifications, enabling proactive measures to be taken.
Temperature control mechanisms, such as refrigeration units, insulated containers, and thermal blankets, are employed during transportation and storage to ensure the products remain within the required temperature range.
Packaging and insulation
Packaging plays a vital role in protecting temperature-sensitive goods from external factors that can affect their quality.
Specialized packaging materials with excellent insulating properties, such as expanded polystyrene foam, vacuum-insulated panels, or phase change materials, are utilized to create a thermal barrier.
These materials help maintain the desired temperature inside the packaging, shielding the products from temperature fluctuations and external heat sources.
Additionally, packaging designs are optimized to minimize heat transfer, prevent moisture ingress, and provide physical protection.
The selection of appropriate packaging solutions depends on factors such as product characteristics, transportation duration, and temperature requirements.
Transporation and storage
Efficient transportation and storage practices are crucial to preserving the freshness and quality of temperature-sensitive goods. Refrigerated vehicles, commonly referred to as reefers, are equipped with temperature control systems to maintain the desired temperature during transit.
These vehicles utilize advanced refrigeration technology, including mechanical refrigeration or cryogenic systems, to provide precise temperature control. Cold storage facilities, such as warehouses and distribution centers, are vital.
These facilities are designed to maintain specific temperature conditions and may include separate temperature zones to accommodate different product requirements.
They feature insulated structures, temperature-controlled chambers, and backup power systems to ensure uninterrupted cold chain operations.
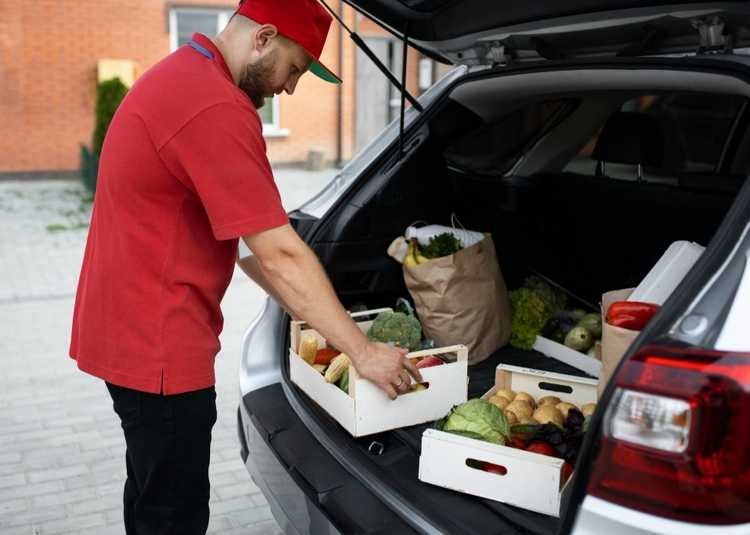

Cold chain management process
Procurement and supplier management
This initial stage focuses on sourcing temperature-sensitive goods from reliable suppliers. It involves conducting thorough assessments of suppliers based on their ability to adhere to quality standards, regulatory requirements, and their capability to maintain the required temperature conditions throughout the supply chain.
Effective supplier management includes establishing clear communication channels, fostering collaborative relationships, and conducting regular audits to verify compliance with temperature control protocols.
By selecting and managing trusted suppliers, organizations can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality temperature-sensitive products.
Inventory management
Proper inventory management is essential in cold chain logistics to optimize stock levels, prevent product expiration, and minimize waste. It involves monitoring inventory levels, tracking expiration dates, and implementing efficient stock rotation practices.
By employing inventory management systems equipped with temperature monitoring capabilities, organizations gain real-time visibility into stock levels and can identify any temperature-related issues that may impact product quality.
This helps ensure that products are used or dispatched in the order of their expiration dates, minimizing the risk of spoilage or loss of potency.
Order fulfillment and distribution
The order fulfillment process begins upon receiving customer orders. This stage encompasses picking, packing, and preparing temperature-sensitive goods for shipment.
It is crucial to ensure proper handling and adherence to temperature control measures during these activities. Packaging materials with insulating properties, such as thermal blankets or refrigerated containers, are employed to maintain the desired temperature conditions during transportation.
Effective route planning and scheduling, considering factors such as distance, temperature requirements, and delivery timeframes, are vital to minimize transit time and ensure product integrity upon arrival at the destination.
Differences Between Cold Chain and Normal Supply Chain
Temperature control
The core distinction between cold chain logistics and a normal supply chain lies in temperature control.
Cold logistics focuses on maintaining precise temperature conditions throughout the entire supply chain to preserve the quality, efficacy, and safety of temperature-sensitive goods.
This requires the use of specialized refrigeration systems, insulated packaging, and temperature monitoring devices. In contrast, a normal supply chain does not prioritize temperature control as goods being transported are typically not sensitive to temperature variations.
Perishable goods
Cold chain logistics primarily deals with perishable goods that have a limited shelf life and are highly susceptible to spoilage or degradation if not handled properly. Examples of such goods include fresh produce, dairy products, seafood, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines.
The time-sensitive nature of these goods requires careful handling, storage, and transportation to ensure they maintain their freshness and effectiveness.
In contrast, a normal supply chain may handle non-perishable goods that do not have strict temperature requirements and can withstand various environmental conditions without affecting their quality or safety.
Time sensitivity
Time sensitivity is a critical factor in cold chain distribution due to the perishable nature of the goods being transported.
Meeting strict time constraints is essential to ensure that products reach their destination within the designated timeframe while maintaining their freshness and efficacy.
Cold chain logistics often operates on tight schedules to minimize the time between production, distribution, and consumption.
In a normal supply chain, while timeliness is important, it may not be as critical as in the cold chain, as the products being transported are not time-sensitive in terms of quality or safety.
Equipment and infrastructure
Cold chain logistics requires specialized equipment and infrastructure to support temperature control and monitoring throughout the supply chain. This includes refrigerated vehicles, cold storage facilities, temperature-controlled packaging, and sophisticated monitoring devices.
The design and functionality of these resources are specifically tailored to maintain the desired temperature conditions and minimize temperature fluctuations.
In a normal supply chain, the focus is more on general transportation and storage equipment, which may not have the specialized temperature control features required for cold logistics.
Compliance and regulations
Cold chain logistics is subject to stringent compliance and regulatory requirements due to the critical nature of maintaining the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive goods.
Regulatory bodies and industry organizations impose specific guidelines and standards for the handling, transportation, and storage of perishable products. Compliance with Good Distribution Practices (GDP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is crucial in cold chain logistics to ensure product integrity and protect public health.
In a normal supply chain, while compliance with regulations is still important, the requirements may not be as specialized or focused on temperature control.
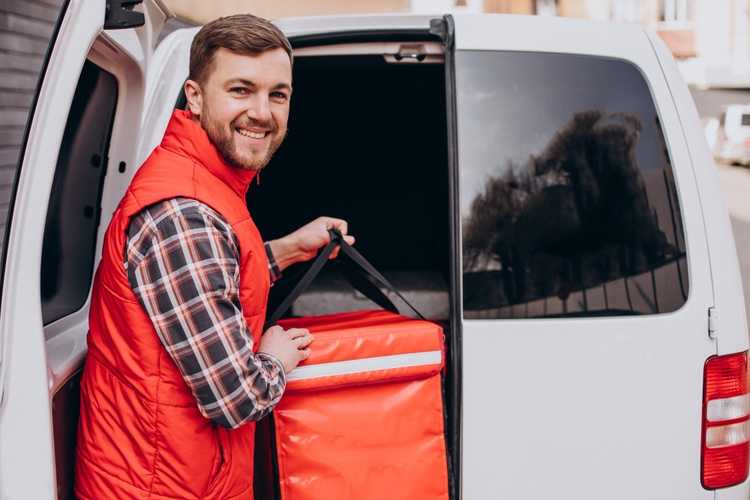

Cold chain logistics use cases
Food and beverage
Food cold chain is instrumental in the food and beverage industry, where it ensures the freshness and safety of perishable products.
From the farm to the consumer’s plate, temperature control is critical in preserving the quality of fresh produce, dairy products, meat, seafood, and frozen goods.
Cold storage facilities, refrigerated transportation, and temperature monitoring systems maintain the optimal conditions necessary to prevent spoilage, maintain nutritional value, and minimize the risk of contamination.
By preserving the quality of food and beverages, cold chain logistics helps extend shelf life, reduces food waste, and safeguards consumer health.
Pharmaceutical and healthcare
The pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors heavily rely on cold chain logistics to maintain the efficacy and safety of temperature-sensitive medications, vaccines, and medical supplies.
These products require strict temperature control throughout the supply chain to prevent degradation and ensure their therapeutic effectiveness.
Cold chain logistics employs specialized refrigerated storage facilities, temperature-controlled packaging, and refrigerated transport to maintain the specified temperature range.
Stringent temperature monitoring, quality control, and regulatory compliance are essential to protect patient health, prevent product damage, and ensure the availability of life-saving medicines.
Floral industry
Cold chain logistics plays a vital role in the floral industry by preserving the freshness and quality of cut flowers during transportation and storage. Flowers are highly perishable and sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Cold logistics employs refrigerated transportation, temperature-controlled storage, and humidity control to extend the shelf life and maintain the aesthetic appeal of flowers.
By minimizing wilting, discoloration, and deterioration, floral logistics ensures that flowers reach consumers, retailers, or event venues in optimal condition, enhancing customer satisfaction and maintaining the value of floral products.
Biotechnology
The biotechnology industry heavily relies on smart cold logistics to maintain the integrity and stability of temperature-sensitive biological samples, reagents, and laboratory supplies.
Biological materials, such as DNA samples, enzymes, antibodies, and other biomolecules, require precise temperature control to prevent degradation and maintain their scientific value. Cold storage facilities, cryogenic freezers, and temperature-controlled transportation systems are used to protect these valuable biotech products.
By ensuring proper temperature management, cold chain logistics contributes to preserving research integrity, supporting accurate diagnostics, and facilitating the development of advanced biotechnological solutions.
Cosmetics and personal care
Certain cosmetic and personal care products benefit from cold chain logistics to preserve their stability and effectiveness. Temperature-sensitive formulations like skincare creams, serums, and specific fragrances may require controlled temperature storage and transportation.
Cold chain logistics ensures that these products do not degrade due to heat exposure, maintaining their desired properties and preventing potential spoilage or reduced efficacy.
By safeguarding product quality and shelf life, cold chain logistics contributes to customer satisfaction and supports the reputation of cosmetic and personal care brands.
Agricultural and horticultural products
Fresh food logistics is crucial in the agricultural and horticultural sectors, where it helps maintain the freshness and quality of perishable goods.
Fruits, vegetables, seeds, seedlings, and other agricultural products require controlled temperature conditions to minimize post-harvest losses, extend shelf life, and preserve nutritional value.
Cold storage facilities, refrigerated transport, and temperature monitoring systems are used to ensure optimal temperature control throughout the supply chain.
By preserving the quality and freshness of these products, cold chain logistics supports food security, reduces waste, and ensures that consumers have access to high-quality produce.
Chemicals and industrial products
Some chemicals and industrial products require specific temperature conditions to maintain their stability and prevent degradation.
Cold chain logistics ensures that temperature-sensitive chemicals, such as adhesives, coatings, and specialty materials, are stored and transported under controlled temperature environments.
By preventing product deterioration or hazardous reactions, cold chain logistics contributes to product quality, safety, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Temperature-controlled storage facilities and refrigerated transportation help maintain the integrity and performance of these chemical and industrial products.
Live animal and veterinary products
Cold chain logistics is essential in the transportation of live animals, including livestock, aquaculture, and pets. Animals require proper temperature control to ensure their well-being and comfort during transport.
Smart cold logistics ensures the provision of temperature-regulated vehicles and appropriate handling procedures to maintain optimal temperature conditions.
Moreover, temperature-sensitive veterinary products such as vaccines, biologicals, and medications require controlled temperature storage and transportation to maintain their potency and effectiveness.
Cold chain distribution in the veterinary field helps ensure the availability of reliable and effective veterinary products while safeguarding animal health.
The Key to Successful Management of Cold Chain Logistics for Perishables
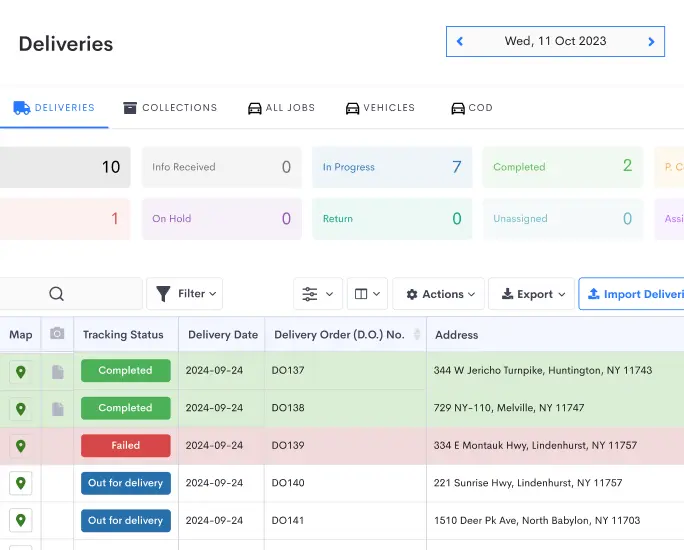
Looking for a game-changer in managing your cold chain logistics for perishable goods? Look no further – Detrack is here to revolutionize your operations.
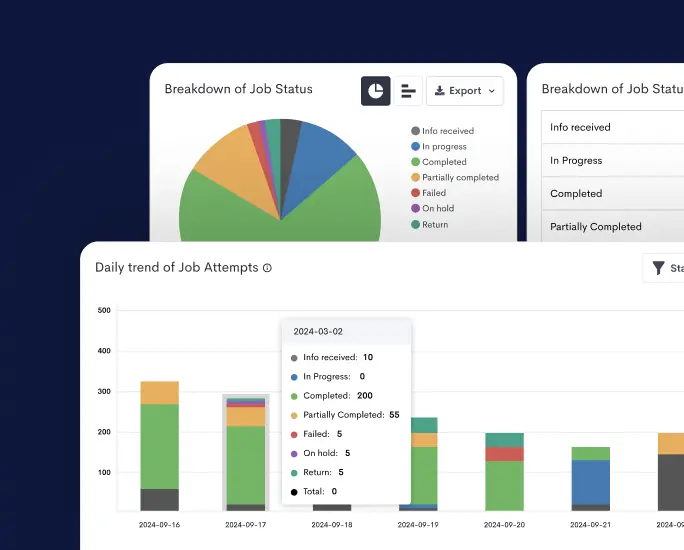
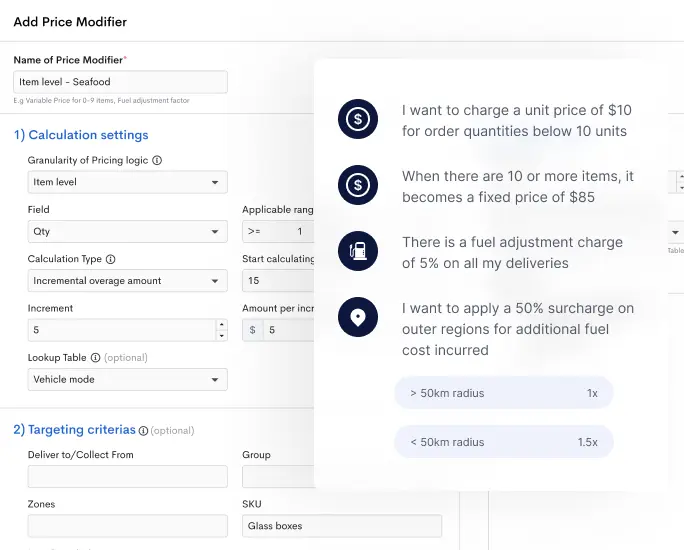
Detrack offers a comprehensive cold chain logistics management solution specifically designed for perishable goods. With its advanced features and user-friendly interface, Detrack empowers you to monitor and track your temperature-sensitive products every step of the way.
Discover real-time, precise location tracking, and detailed delivery status updates in one powerful platform. Say goodbye to costly temperature excursions, inventory losses, and customer dissatisfaction.
Experience the peace of mind that comes with seamless cold chain logistics management. Take your business to new heights of efficiency, reliability, and customer satisfaction with Detrack.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to transform your perishable goods logistics. Click here to unlock the power of Detrack and elevate your cold chain management success today!