Have you ever wondered why shipping is so expensive? The shipping costs can exceed the product’s price often when you order something online. It’s enough to make you want to give up on buying anything online!
But what many people don’t realize is that there are a lot of factors that go into calculating shipping costs. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at why shipping is so expensive.
The Anatomy of Shipping Costs
If you’re wondering why shipping costs so much, here are the things that are included in it:
Transportation and Fuel Charges
The mode of transportation is a significant cost driver. Shipping by truck, ship, plane, or train comes with unique cost structures. For example, shipping by air is generally faster but more expensive than shipping by sea.
Transportation costs also include vehicle maintenance, which is crucial to ensure the safety and reliability of the shipping fleet.
Moreover, if a company doesn’t own its vehicles, leasing or purchasing costs for vehicles must be factored in.
Labor and Handling Fees
Labor costs are a substantial part of shipping expenses. It encompasses the wages and salaries of the personnel involved in the shipping process, from drivers and warehouse workers to administrative staff.
Labor costs can vary based on geographical location and labor market conditions. Handling fees come into play during loading and unloading processes and using specialized equipment like forklifts or cranes.
Packaging Material and Costs
Packaging materials and their associated costs are vital to protecting goods during transit. The choice of packaging materials can significantly impact costs and the safety of the shipped items.
For example, fragile or sensitive goods may require more elaborate and costly packaging to prevent damage. Selecting the right packaging materials and optimizing the quantity used can help businesses balance protecting their products and keeping shipping costs in check.
Import and Export Taxes
When dealing with international shipments, import and export taxes, duties, and customs fees become a critical consideration. Government authorities typically levy these fees and can vary widely depending on the destination country and the nature of the goods being shipped.
Proper understanding of the applicable tariffs and duties is essential for accurate cost estimation and compliance with international trade regulations.
Warehousing and Storage Fees
Temporary storage of goods in a warehouse or storage facility before or after shipping can add to overall shipping expenses.
The cost of warehousing and storage depends on factors like the duration of storage, the volume of goods, and the location of the facility. Efficient inventory management and logistics planning can help reduce these costs.
Insurance Costs
Shipping insurance is essential to protect against unforeseen events such as damage, loss, or theft during transit. The cost of insurance premiums depends on the value of the goods being shipped and the level of coverage required.
It’s important to carefully assess the value of the goods, the potential risks, and the cost of insurance to strike the right balance between protection and expenditure.
Distance and Route Complexity
The distance between the origin and destination significantly affects shipping costs. Longer distances generally result in higher transportation expenses, requiring more time and resources.
Additionally, the complexity of the shipping route, including challenges like navigating through remote or hazardous areas, can add to the cost. Route planning and optimization can help reduce these costs and ensure timely deliveries.
External Factors Driving Up Costs
Here are some of the external factors on why is shipping so expensive:
Fluctuations in Global Oil Prices
Fluctuations in global oil prices directly and immediately impact shipping costs. The shipping industry heavily relies on bunker fuel derived from crude oil.
When oil prices rise, bunker fuel costs increase, elevating operational expenses for shipping companies. To mitigate the impact of higher fuel costs, shipping companies may adjust their pricing structures by increasing shipping rates.
This, in turn, can affect the overall cost of goods and consumer prices, making oil price volatility a significant factor in the global shipping industry.
Changes in Regulatory and Environmental Policies
Environmental and regulatory policies have become increasingly stringent in recent years to combat climate change and reduce emissions from the shipping sector.
These policies often require shipping companies to adopt cleaner, more expensive fuels such as low-sulfur marine fuels or invest in technologies that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
While these initiatives are crucial for environmental sustainability, they have higher operational costs. Shipping companies pass these additional expenses on to customers through higher shipping rates as they strive to adhere to environmental standards and meet compliance requirements
Seasonal Demands and Constraints
The shipping industry experiences seasonal variations in demand due to holidays, weather conditions, and agricultural harvests. During peak seasons, such as the holiday season, there is a surge in consumer goods shipments.
This heightened demand can lead to a shortage of available cargo space, pushing shipping rates.
Conversely, during off-peak periods, when demand is lower, shipping rates may decrease as shipping companies seek to fill empty vessels and maximize their revenues.
These seasonal fluctuations directly impact the cost of shipping and can influence the timing of deliveries and inventory management for businesses.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Tariffs
Another factor why is shipping so expensive is geopolitical tensions and trade tariffs. When trade tensions rise between countries, they may impose tariffs or embargoes on specific goods or trading partners.
These disruptions can lead to changes in shipping routes, longer transit times, increased security measures, and additional administrative burdens. All these factors contribute to higher shipping costs as shipping companies adjust to new circumstances and challenges in the global trade environment.
Moreover, the uncertainty created by geopolitical tensions can affect the stability of trade relationships and long-term planning for shipping companies.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates play a pivotal role in international shipping costs. When a domestic currency strengthens relative to foreign currencies, it can make imports cheaper for the country.
Conversely, a stronger domestic currency can make a country’s exports more expensive for international buyers. This fluctuation can lead to shifts in the balance of trade and alter shipping patterns. Importers and exporters must consider exchange rate fluctuations when pricing goods, as it directly influence their competitiveness in international markets.
For instance, a stronger domestic currency might reduce the demand for exports, leading to decreased shipping volumes and potentially higher shipping costs per unit of goods.
The Impact on Business Owners and Wholesalers
Here is how expensive shipping costs can impact business owners and wholesalers:
Price Increases and Customer Pushback
When shipping costs rise due to fluctuating oil prices, regulatory changes, or geopolitical tensions, business owners and wholesalers often find themselves in a challenging position.
To offset increased shipping expenses, they may need to raise the prices of their products or pass on the additional shipping costs to their customers. However, this can lead to customer pushback as higher prices may make their products less competitive or affordable.
Business owners must strike a delicate balance between maintaining profitability and satisfying customer expectations. Price increases, especially in highly competitive markets, can pressure businesses to provide additional value to justify the higher costs
Inventory Management and Cash Flow
Increasing shipping costs can disrupt inventory management and cash flow for wholesalers and business owners. To minimize the impact of rising shipping costs, businesses may consider ordering larger quantities of goods in advance.
However, this can tie up capital in inventory and affect cash flow. Alternatively, they might choose to keep lower inventory levels, which can lead to supply chain delays or stockouts if not managed effectively.
Balancing inventory levels and cash flow becomes a complex task, and businesses may need to invest in more sophisticated supply chain and inventory management systems to optimize their operations.
Competitive Disadvantages
Higher shipping costs can put businesses at a competitive disadvantage, especially when competing with companies that have more favorable shipping terms or lower operational costs.
Businesses operating on thin profit margins may find it challenging to absorb increased shipping expenses without compromising competitiveness. This can lead to a loss of market share or reduced profitability.
In some cases, businesses may explore alternative strategies, such as renegotiating shipping contracts, seeking more cost-effective shipping solutions, or diversifying their supplier and distribution networks to maintain a competitive edge.
Challenges in International Market Expansion
For businesses looking to expand into international markets, the impact of external shipping cost factors can be even more pronounced. Fluctuating currency exchange rates, trade tariffs, and geopolitical tensions can create barriers to entry or expansion.
These factors may complicate international market strategies and increase the complexity of cross-border logistics.
Businesses seeking international expansion need to conduct thorough market research, assess the impact of shipping costs on their international pricing strategies, and develop contingency plans to navigate geopolitical uncertainties effectively.
Strategies to Counteract High Shipping Costs
Shipping is expensive, but there are ways to counteract it. Here are some of them:
Negotiating Contracts with Carriers
- Build strong relationships with shipping carriers and negotiate long-term contracts. This can often lead to volume discounts or more favorable rates.
- Consider using a third-party logistics (3PL) provider, which may have established carrier relationships and can negotiate better rates on your behalf.
- Be aware of carrier rate increases and negotiate terms that protect your business from unexpected cost hikes.
Optimizing Packaging for Efficiency
- Evaluate your packaging materials and design to minimize excess weight and dimensions. Smaller, lighter packages can lead to lower shipping costs.
- Implement packaging automation to ensure consistency and minimize waste.
- Consider sustainable packaging options that are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Diversifying Supply Chain and Distribution Networks
- Expand your supplier base to include multiple vendors or sources for critical components or products. This can help mitigate supply chain disruptions.
- Use multiple distribution centers strategically located to reduce shipping distances and costs.
- Utilize dropshipping, cross-docking, or third-party fulfillment centers to reduce inventory carrying costs.
Leveraging Technology for Route Optimization
- Invest in route optimization software to find the most efficient delivery routes. These tools take into account factors like distance, traffic, and fuel costs.
- Utilize real-time tracking and monitoring of shipments to address issues as they arise and avoid additional costs.
- Implement demand forecasting and inventory management software to minimize the need for expedited shipping.
Encouraging Bulk Purchases or Minimum Purchase Values
- Offer discounts or incentives for customers who make bulk purchases or meet minimum order values. This can help consolidate shipments and reduce per-unit shipping costs.
- Set clear minimum order requirements for wholesale or business customers to encourage larger purchases.
- Implement tiered pricing structures that reward larger orders with better pricing.
Staying Ahead: Preparing for Future Shipping Challenges
In conclusion, the answer to, “why is shipping so expensive?”, is the result of a complex interplay of factors. The global logistics network involves numerous intermediaries, fuel price fluctuations, environmental regulations, trade complexities, and the demands of e-commerce. These elements collectively drive up expenses for both businesses and consumers.
While shipping costs may always be a challenge, there are strategies for mitigating them, such as negotiation, packaging optimization, and sustainable choices. The industry must also adapt to new technologies and sustainability measures to reduce shipping costs.
Understanding these dynamics and actively seeking cost-saving measures is crucial for navigating the world of shipping effectively. It may not become drastically cheaper, but with informed choices and industry innovation, it can become more manageable for all stakeholders.
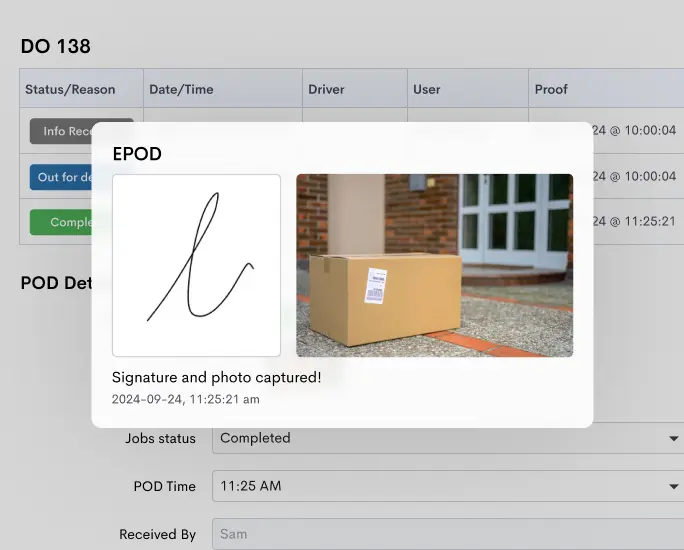
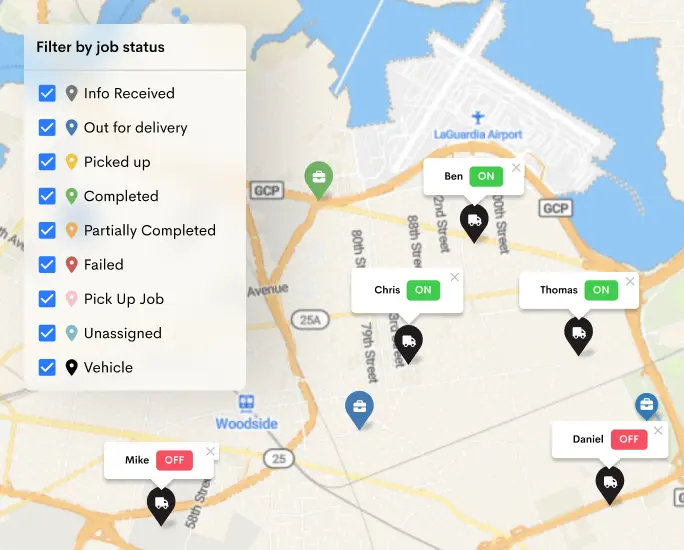
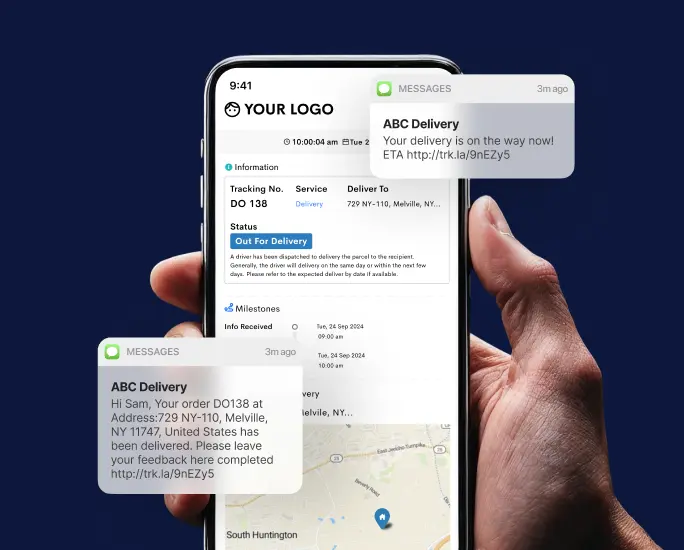
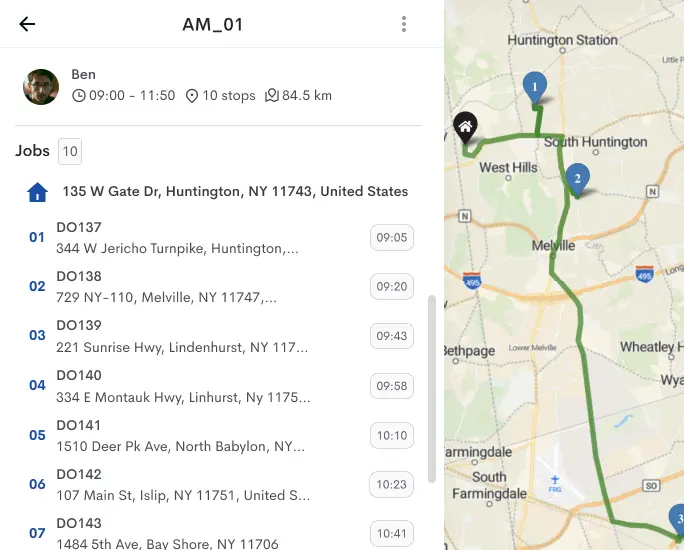
If you want to cut down shipping costs in your delivery business, Detrack can be a crucial ally. Our software implementation offers several advantages, including reduced paper expenses through E-Pod, real-time notifications that decrease customer inquiries, leading to a leaner administrative team, and improved fleet monitoring for enhanced performance. These are just some of the outstanding benefits you can enjoy.