As we enter 2024, businesses continue to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of supply chains. In this era of technological advancements, consumer demands, and global shifts, staying ahead requires a keen eye on emerging trends.
The supply chain arena is poised for significant transformations from sustainability to automation, transparency to resilience.
In this blog post, we’ll explore 20 pivotal supply chain trends businesses must watch closely in 2024. These trends promise to shape strategies, redefine operations, and drive innovation, paving the way for a more agile and responsive supply chain ecosystem.
20 Supply Chain Trends to Watch For
Sustainability and Ethical Supply Chains
Sustainability has transitioned from a trend to a core business principle. In response to growing environmental concerns and consumer demand, supply chains are pivoting towards ethical and sustainable delivery practices.
This encompasses a holistic approach that involves reducing carbon footprints, minimizing waste, adopting renewable energy sources, and ensuring ethical materials sourcing. Companies are integrating eco-friendly materials into their products, embracing recycling initiatives, and rethinking packaging to minimize environmental impact.
Ethical supply chains also prioritize fair labor practices, supporting workers’ rights, and fostering transparent supplier relationships. Businesses that prioritize sustainability meet regulatory requirements and resonate with a socially conscious consumer base, creating long-term brand loyalty and positive societal impact.
Digital Transformation
The transformation of supply chains is an ongoing revolution emphasizing data-driven decision-making and process automation. This transformation leverages advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, big data analytics, and digital twins to create interconnected and intelligent supply chain networks.
IoT devices collect real-time data from various touchpoints, enabling predictive analytics and proactive decision-making. Cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless collaboration among supply chain partners, optimizing inventory management and enhancing visibility across the entire supply chain ecosystem.
Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, enable simulation and optimization, allowing businesses to forecast outcomes and make informed decisions swiftly. Integrating these digital technologies enhances operational efficiency, agility, and responsiveness, driving competitive advantage in a rapidly changing market.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications continue to revolutionize supply chain management by optimizing various processes. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets, predict demand patterns, optimize route planning, and enable dynamic pricing strategies.
Machine learning algorithms enhance inventory management by predicting demand fluctuations, minimizing excess inventory, and reducing holding costs. Predictive analytics powered by AI and ML facilitate proactive maintenance, ensuring equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
These technologies enable supply chains to adapt to market fluctuations, enhance forecasting accuracy, and optimize resource allocation. Additionally, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants improve customer service, enabling faster query resolution and enhancing overall customer experience within the supply chain.
Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology has gained traction for its potential to revolutionize supply chain transparency and traceability. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain ensures the authenticity and transparency of transactions across the supply chain.
By creating a secure and transparent ledger, blockchain technology enhances stakeholder trust, authenticates product provenance, and safeguards against counterfeiting. This technology is particularly instrumental in industries where traceability is crucial, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Blockchain’s ability to securely track and trace products throughout their lifecycle ensures compliance with regulatory standards, mitigates risks associated with counterfeit goods, and strengthens the integrity of supply chain networks.
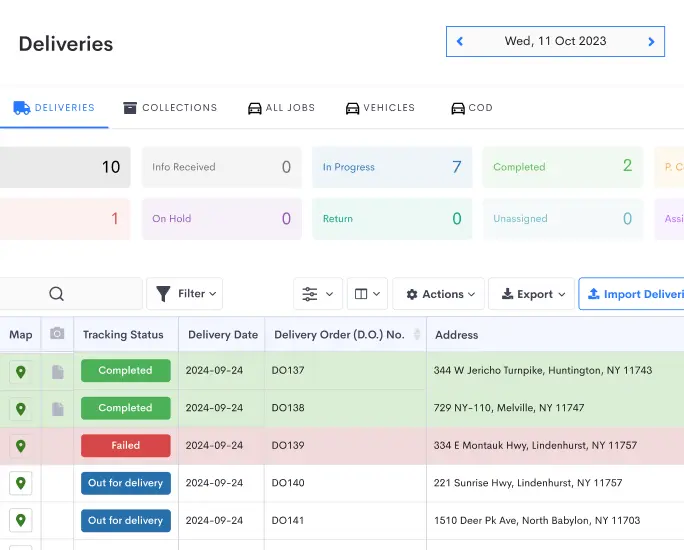
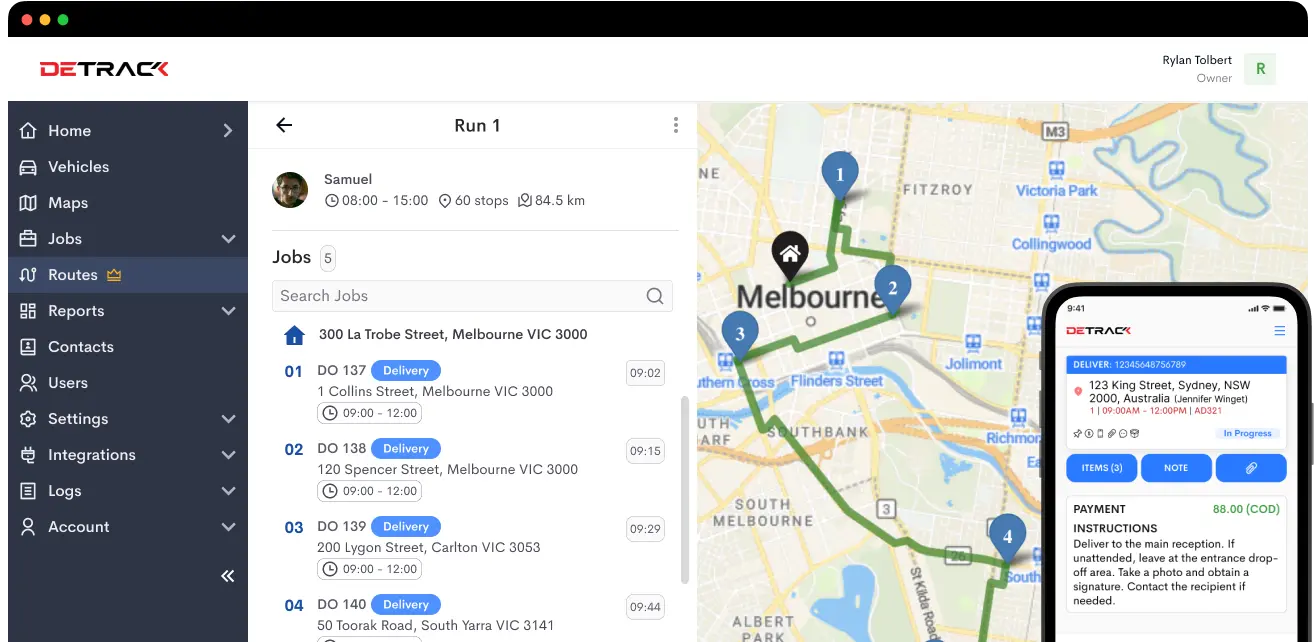
Supply Chain Visibility
Real-time visibility across the supply chain is critical for informed decision-making and proactive problem-solving. Advancements in sensor technology, RFID, GPS, and IoT devices provide granular insights into every stage of the supply chain.
These technologies enable businesses to track shipments, monitor inventory levels, and optimize transportation routes in real time. Enhanced visibility allows for identifying potential bottlenecks, mitigating disruptions, and optimizing inventory levels.
Real-time insights empower supply chain managers to make data-driven decisions, reduce lead times, and improve operational efficiency. Furthermore, increased transparency fosters stakeholder collaboration, enabling a more agile and responsive supply chain ecosystem.
Cybersecurity
The increasing digitization and interconnectivity of supply chains have elevated the importance of robust cybersecurity measures. Protecting sensitive data, securing communication channels, and safeguarding against cyber threats are paramount.
Cybersecurity measures encompass encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices. The consequences of a cybersecurity breach in a supply chain can be severe, ranging from data compromise and operational disruptions to financial losses and reputational damage.
Therefore, investments in cybersecurity infrastructure and stringent protocols are crucial to ensure the integrity and resilience of supply chain operations.

Hyperautomation
The integration of AI, ML, robotics, and process automation leads to hyperautomation within supply chains. This trend aims to automate complex, repetitive tasks across the supply chain ecosystem. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines workflows by mimicking human actions, reducing manual errors, and enhancing operational efficiency.
AI-driven automation tools optimize demand forecasting, inventory management, and order processing. Machine learning algorithms continuously learn and adapt, enabling predictive analytics and optimizing decision-making processes.
Hyperautomation not only improves productivity but also frees up human resources to focus on strategic tasks that require creativity and critical thinking, ultimately driving innovation within supply chains.
Circular Supply Chains
Circular supply chains emphasize the concept of a circular economy, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. Businesses are rethinking product design, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life strategies to achieve a closed-loop system.
This involves designing products that are durable, repairable, and recyclable. Recycling initiatives and the use of recycled materials reduce the environmental footprint of products. factors. Furthermore, initiatives to refurbish and remanufacture products extend their lifecycle, contributing to resource conservation and waste reduction.
Circular supply chains align with sustainability goals and present opportunities for cost savings, innovative business models, and enhanced brand reputation as environmentally responsible entities.
Regionalization of Supply Chains
The shift towards regional and localized supply chains aims to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions, reduce transportation costs, and enhance customer responsiveness. By decentralizing manufacturing and sourcing closer to end markets, businesses can adapt more swiftly to changing consumer demands.
Regionalization also addresses concerns related to geopolitical tensions, trade tariffs, and transportation challenges associated with global supply chains. Furthermore, proximity to consumers reduces delivery lead times and supports just-in-time inventory management.
This trend fosters stronger relationships with local suppliers, encourages sustainability by reducing carbon emissions from long-distance transportation, and enables businesses to cater more effectively to regional preferences and regulations.
Rationalizing the Supply Base
Rationalizing the supply base involves streamlining supplier relationships and strategically reducing third-party dependencies. Businesses aim to enhance operational efficiency and reduce risks by consolidating and optimizing the supplier network.
This approach allows for better negotiation leverage, standardized processes, and improved collaboration with a smaller pool of trusted suppliers. Rationalizing the supply base also simplifies procurement processes, reducing administrative burdens and costs associated with managing multiple vendors.
Additionally, closer relationships with a selected group of suppliers enable deeper collaboration, fostering innovation, and co-development initiatives that drive mutual growth and competitiveness.
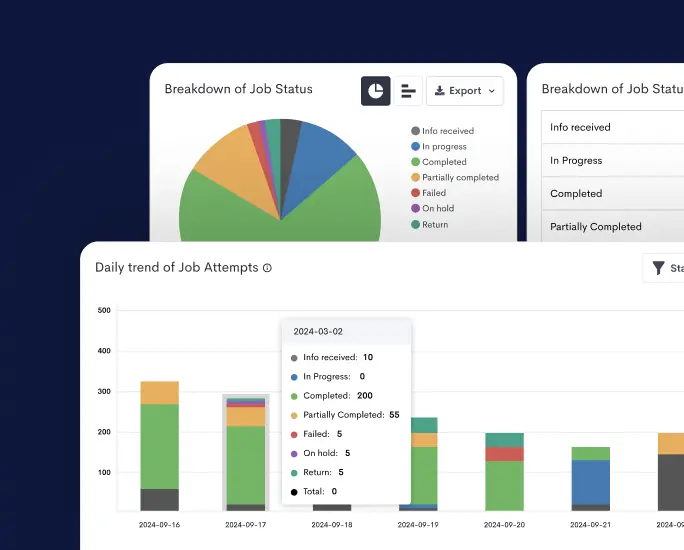
Improving Risk Prediction and Management
Advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and predictive models enable businesses to anticipate, assess, and mitigate risks effectively. Companies can proactively identify potential vulnerabilities and disruptions within the supply chain by analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors.
Predictive analytics provide early warning signals for supply chain disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical events, supplier failures, or unexpected demand fluctuations. This foresight allows businesses to develop robust risk mitigation strategies, build resilience, and ensure continuity in operations.
Companies with sophisticated risk management capabilities can respond swiftly and decisively to unforeseen challenges, minimizing the impact on supply chain performance and maintaining customer satisfaction.
3D Printing in Manufacturing
The adoption of additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, is revolutionizing traditional manufacturing processes within supply chains. This technology allows for producing complex parts and components on demand, reducing reliance on conventional manufacturing methods.
3D printing enables rapid prototyping, customization, and decentralized manufacturing closer to end markets. By eliminating the need for large-scale inventory storage and tooling, 3D printing significantly reduces lead times and production costs.
This innovation also facilitates the creation of spare parts, addressing supply chain disruptions caused by inventory shortages or long lead times for replacement components. Additionally, 3D printing promotes design flexibility, sustainability, and innovative product development within supply chains.

Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are transforming supply chain operations by enhancing training, maintenance, and remote assistance. Within warehouses, AR applications provide hands-free guidance to workers, improving picking accuracy and efficiency.
VR simulations enable immersive training experiences, allowing employees to practice complex tasks in a virtual environment. Maintenance technicians with AR-enabled devices can access real-time instructions and remote assistance, reducing downtime and enhancing equipment repair efficiency.
Moreover, AR and VR technologies facilitate interactive customer experiences, enabling virtual product demonstrations and enhancing customer engagement. Embracing AR and VR in supply chains enhances workforce productivity, reduces errors, and fosters a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
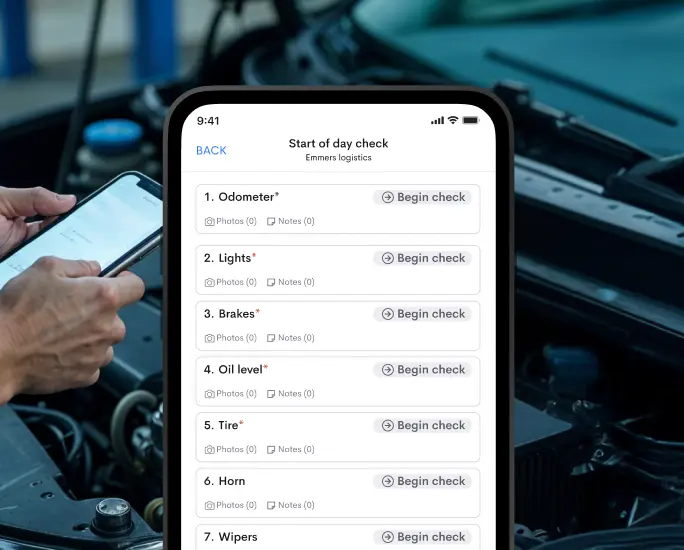
Predictive Maintenance
Further advancements in predictive maintenance leverage IoT sensors and AI algorithms to forecast supply chain equipment failures and maintenance requirements. These technologies enable condition-based monitoring, detecting anomalies and potential failures before they occur.
Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze equipment performance data in real-time, predicting the remaining useful life of machinery and components. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical assets.
By implementing predictive maintenance strategies, businesses ensure operational continuity, optimize asset performance, and enhance supply chain reliability.
Supplier Diversity and Inclusion
Promoting supplier diversity and fostering inclusive practices within supply chains contribute to innovation, resilience, and social responsibility. Supplier diversity initiatives involve partnering with businesses owned by minorities, women, veterans, and other underrepresented groups.
Embracing supplier diversity fosters innovation through diverse perspectives and experiences, driving creativity and competitiveness within the supply chain. Supplier diversity initiatives promote economic inclusion, empowering underrepresented communities and supporting local businesses.
Businesses prioritizing supplier diversity and inclusion create a more robust and adaptive supply chain ecosystem while positively impacting society.
Last-Mile Delivery Innovations
Innovative solutions in last-mile delivery, such as drones, autonomous vehicles, and delivery robots, are revolutionizing logistics and customer service within supply chains. Autonomous vehicles and drones enable faster and more efficient delivery, especially in urban areas.
These technologies reduce delivery times, lower transportation costs, and enhance customer experience. Delivery robots navigate sidewalks and deliver parcels to customers’ doorsteps, reducing the need for human intervention in the last mile.
Additionally, smart delivery lockers and alternative pickup locations provide flexibility and convenience to customers. Last-mile delivery innovations optimize logistics operations, reduce carbon emissions, and address challenges associated with congested urban areas.
Climate-Resilient Supply Chains
Building resilience against climate-related disruptions is becoming increasingly vital within supply chains. Climate risk assessments enable businesses to identify vulnerabilities and develop mitigation strategies to withstand extreme weather events, natural disasters, and long-term climate changes.
Diversifying sourcing strategies and supply chain locations minimizes exposure to climate-related risks in specific regions. Investing in infrastructure and technology that can withstand climate-related challenges ensures operational continuity.
Moreover, implementing sustainable practices, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting renewable energy sources, contributes to climate resilience while aligning with environmental sustainability goals. Businesses committed to climate-resilient supply chains ensure operational stability and contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
Predictive Analytics for Demand Sensing
Leveraging predictive analytics for demand sensing enables businesses to anticipate and respond to shifting market demands. Advanced algorithms analyze historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to predict consumer behavior and demand patterns.
Predictive demand analytics enable businesses to optimize inventory levels, improve forecasting accuracy, and align production schedules with anticipated demand. These insights empower supply chain managers to make informed decisions regarding procurement, production, and distribution, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.
By deploying predictive analytics for demand sensing, businesses enhance their agility, reduce supply chain disruptions, and improve overall operational efficiency.

Regulatory Compliance and Supply Chain Ethics
The focus on regulatory compliance and ethical practices within supply chains has intensified. Adhering to evolving regulations and ethical standards ensures compliance with labor laws, fair trade practices, and responsible sourcing methodologies.
Businesses are investing in supply chain transparency initiatives to trace the origin of raw materials and ensure ethical sourcing practices. Additionally, compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability certifications is gaining prominence.
A commitment to ethical supply chain practices mitigates legal risks, enhances brand reputation, and fosters trust among consumers and stakeholders. Companies prioritizing ethical supply chain practices exhibit corporate responsibility, resilience, and long-term sustainability in their operations.
Moving Beyond Real-Time Analytics to Real-Time Execution
2024 presents many transformative trends and opportunities for businesses worldwide. Embracing these 20 supply chain trends is crucial for staying competitive, fostering innovation, and driving sustainable growth.
The convergence of technology, sustainability, and strategic adaptation will define the success stories in supply chain management. Businesses that navigate these trends effectively will optimize operational efficiency and build resilient, agile, and socially responsible supply chains.
As the market continues to evolve, the ability to innovate, adapt, and leverage these advancements will be pivotal in staying ahead in the dynamic and ever-changing world of supply chain management.